ongoing project
virtual trichrome
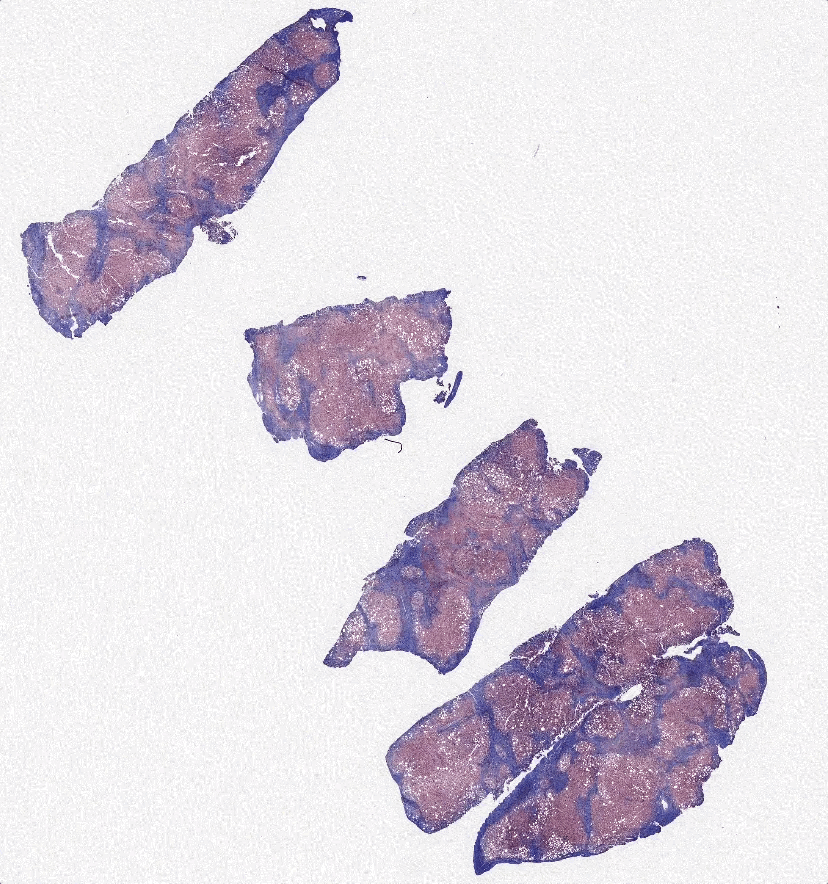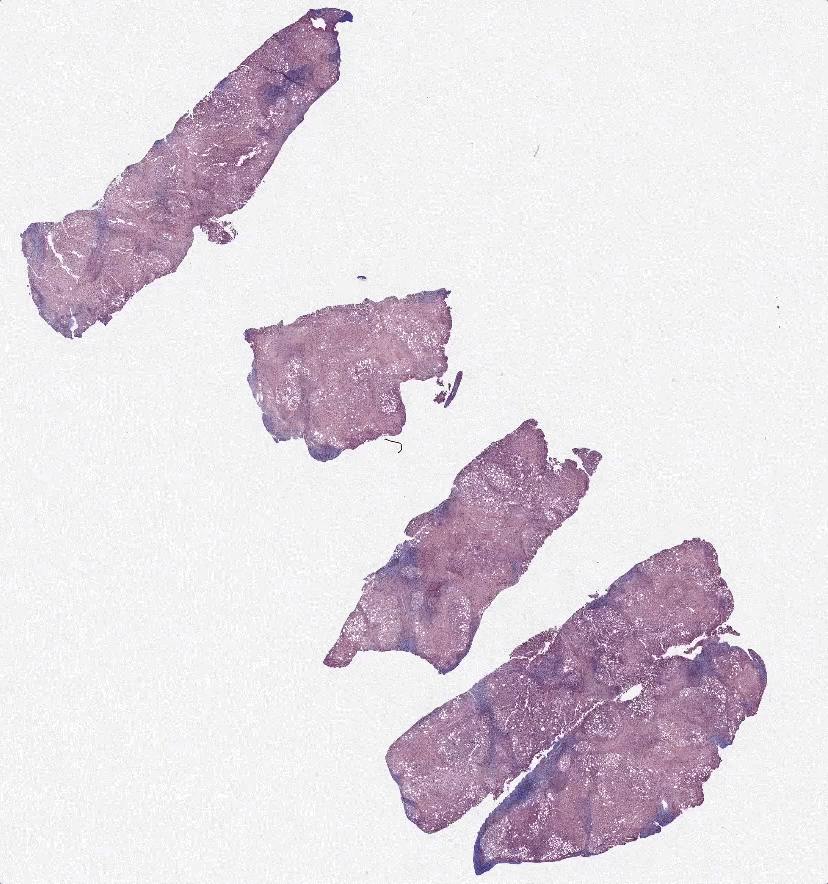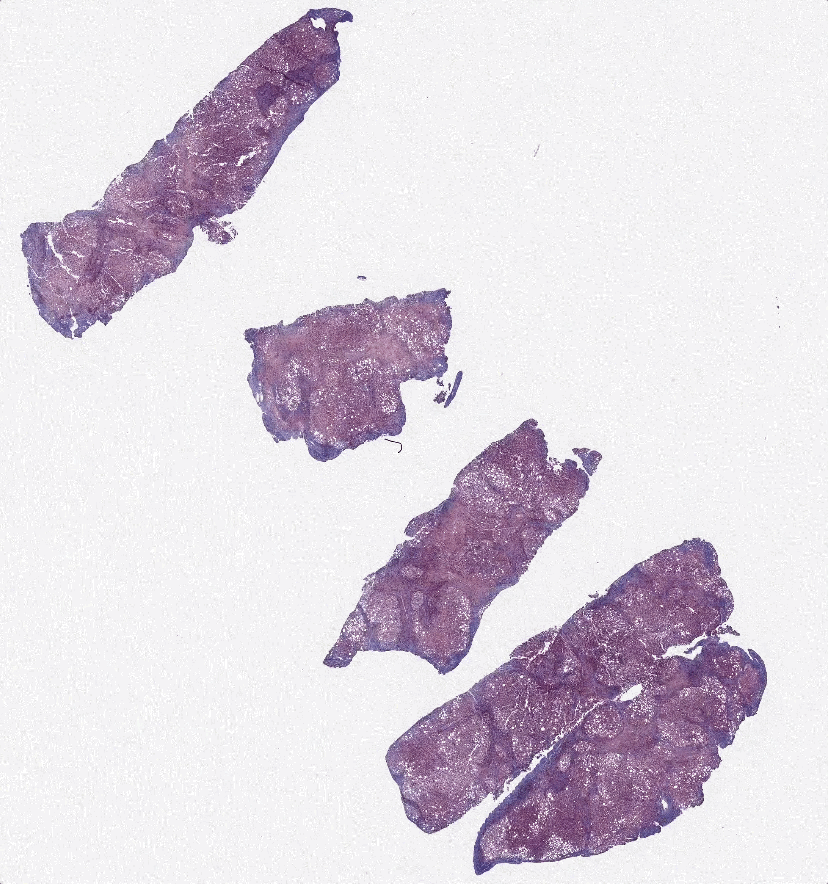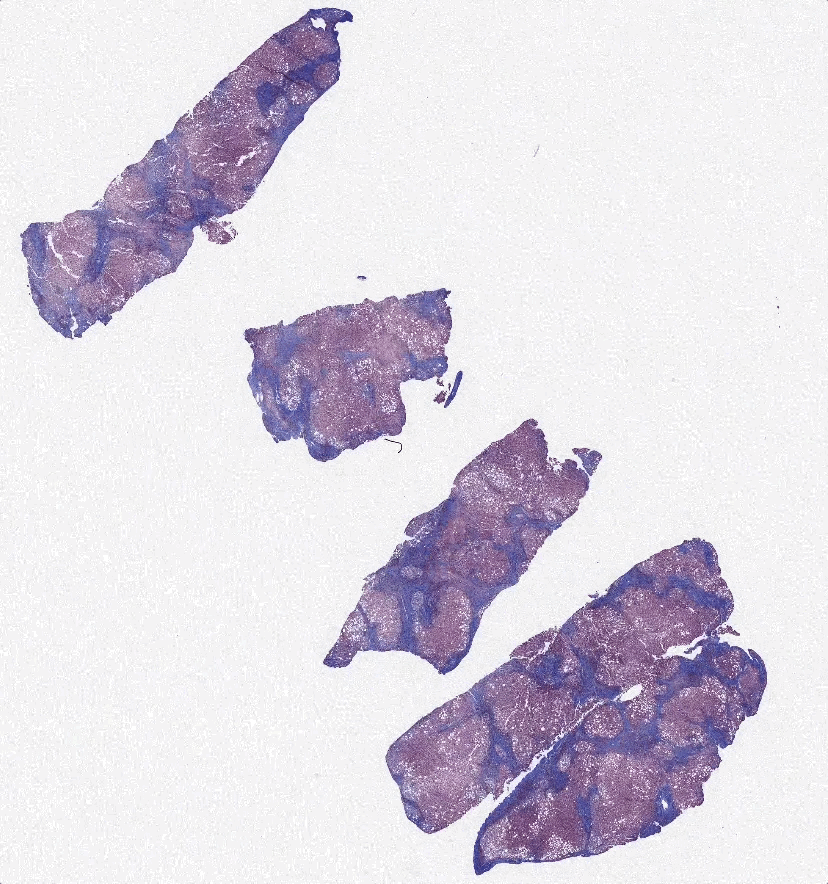
Scientific Premise:
That a set of generative adversarial networks can trained with imperfectly registered image pairs to convert H&E stains to trichrome stains.
Motivation:
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) is a prevalent liver inflammation disease that affects over 16 million US adults. Patients diagnosed with NASH have no alcoholic, genetic, metabolic, or medication-based causes for hepatitis and typically experience progressive liver injury and fibrosis. NASH can lead to cirrhosis, liver transplant and death, while the burgeoning incidence places a significant financial toll on the healthcare system. NASH is diagnosed using an H&E section, where Pathologists assess for indications of hepatocyte damage (e.g., ballooning, pockets of inflammation), while Fibrosis progression is typically assessed via a Trichrome stain of liver biopsy (e.g., bridging between Portal regions). The process of staining, destaining, and restaining the same tissue regions can be time-consuming, expensive, and inaccurate.
Advances in generative adversarial networks (GANs) offer a potential solution to this issue. GANs use two neural networks to generate images. The first neural network creates an image of the target type, while the second neural network discriminates whether or not a given image is real or generated. GANs such as CycleGAN and Pix2Pix have been able to effectively convert images of similar objects into each other. An increasing number of medical studies have used GANs to synthetically stain tissue.
As a result, GANs are a promising method to synthetically generate trichrome stains of tissue from H&E stains. However, one issue with using Pix2Pix for this purpose has been the imperfect registration and artifacts in paired images. These issues inflate the L1 loss, which causes “hallucinations” in the generated images. Still, Pix2Pix and CycleGAN are promising platforms to synthetically stain tissues. We believe that a generative model that incorporates paired training images and reconstruction loss will allow it to retain the structural accuracy of Pix2Pix, while also reducing hallucinations through cycle-consistency.
Manuscripts:
- Levy, J., Jackson, C., Sriharan, A., et al. Preliminary Evaluation of the Utility of Deep Generative Histopathology Image Translation at a Mid-sized NCI Cancer Center. Proceedings of the 13th International Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems and Technologies (BIOSTEC 2020) - Volume 3: BIOINFORMATICS 3, 302–311 (2020).
- Levy, J. J., Azizgolshani, N., Andersen, M. J., et al. A large-scale internal validation study of unsupervised virtual trichrome staining technologies on nonalcoholic steatohepatitis liver biopsies. Modern Pathology 34, 808–822 (2021).
Awards: - BIOSTEC 2020 Comp2Clinic Best Paper Award
- Modern Pathology Top Picks January 2021